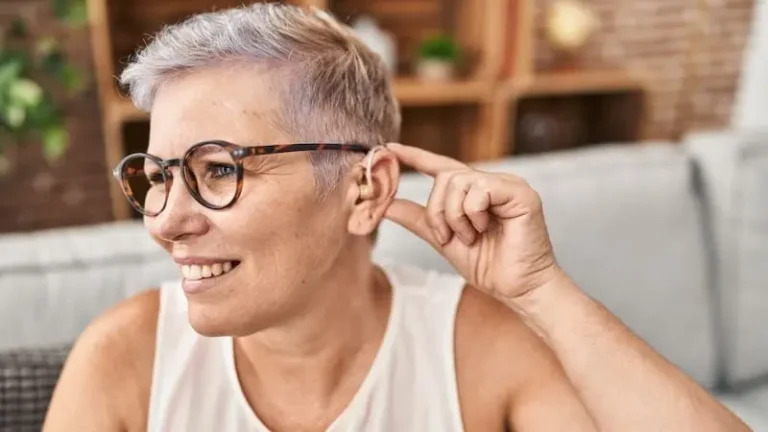
A hearing aid is a type of miniature sound amplification device that amplifies external sounds to the desired level for patients with hearing loss. By utilizing the residual hearing the patient for hearing compensation, it enables patients with hearing loss to hear sounds as well as people with normal hearing, making it the most effective tool currently available for improving the hearing of majority of patients with mild, moderate, and severe deafness. Hearing aids come in a wide variety, but despite their small size, they all contain: 1. Micro; 2. Chip; 3. Amplifier; 4. Battery; 5. Receiver.
.webp)
Sound signals are converted into electrical signals by microphones, amplified by amplifiers, and then restored into sound signals by receivers to be transmitted to the human ear The working principle of hearing aids is the process of acoustic-electric conversion, which amplifies different frequencies of sound according to different hearing loss conditions, so as to achieve the effect ofifying small sounds without making loud sounds noisy. In the process of sound processing, hearing aids use intelligent noise reduction technology, binaural fusion, dual microphones and other new technologies improve hearing conditions, especially the clarity of speech in noisy environments.